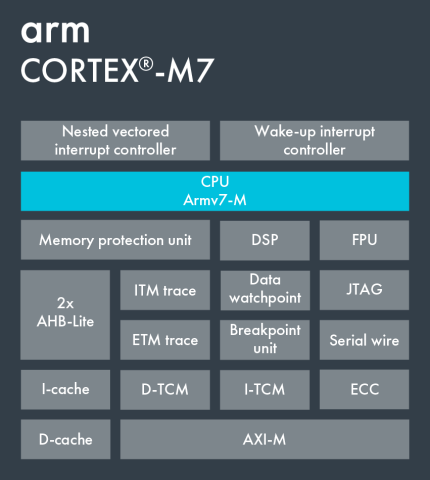
Cortex-M7
The Cortex-M7 implements the ARMv7E-M architecture using a 6 stage superscalar pipeline with branch prediction, instruction and data caches (64 bit buses) and tightly coupled memories (TCMs) to give nearly double the performance of M4 processor.
Double precision instructions are added to the IEEE 754 compliant Floating Point Unit, Digital Signal Processing (DSP) and Thumb-1 and Thumb-2 instructions.
A Memory Protection Unit supporting 8 or 16 protection regions to separate processes and privileges.
The bus mechanism implements a 64-bit AMBA4 AXI, 32-bit AHB peripheral (AHBP) port, 32-bit AHB slave (AHBS) port for external master (such as DMA controller) to access Tightly-Coupled Memories and APB interface for debug.
The Nested Vector Interrupt Controller (NVIC) supports up to 240 interrupt inputs from peripherals with programmable priority levels from 8 to 256 levels.
Optional Instruction (Embedded Trace Macrocell), Data Trace (DWT), and Instrumentation Trace (ITM), JTAG and Serial Wire Debug ports. Up to 8 breakpoints and 4 watchpoints.
Explore This Technology
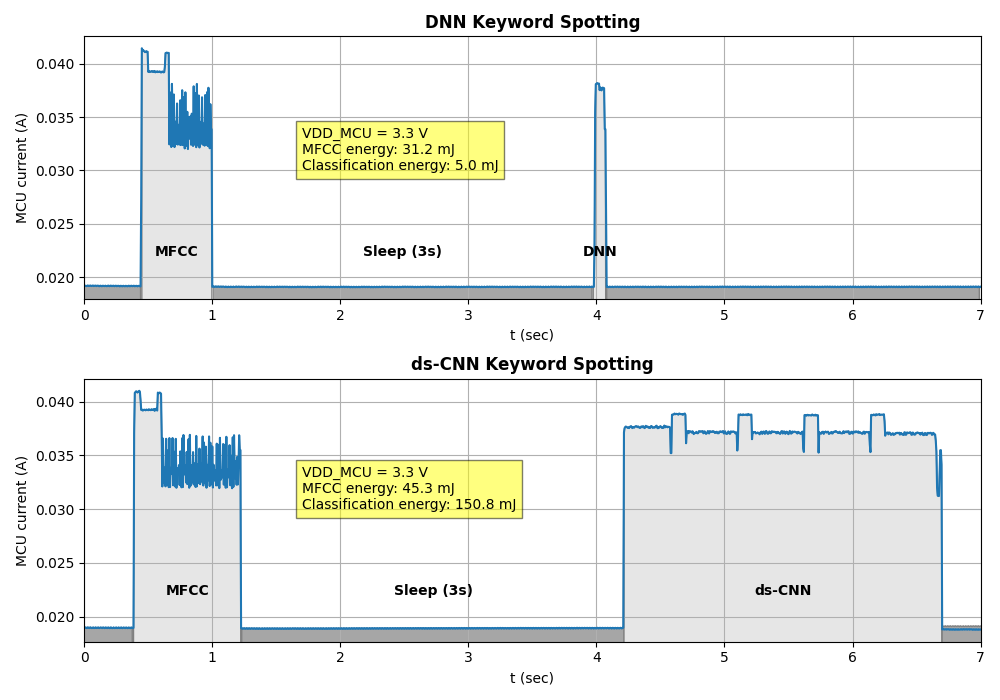
Projects Using This Technology














Add new comment
To post a comment on this article, please log in to your account. New users can create an account.