This project aims to develop an advanced RF energy harvesting (EH) receiver chip specifically designed to power embedded sensors for monitoring the condition of groceries during transportation. The receiver chip captures wireless energy transmitted from phased array antennas and converts it into electrical power that is used to operate onboard sensors, which continuously monitor critical parameters such as temperature and humidity inside delivery trucks.
View Competition: Collaboration/Education Projects
In the context of Industry 4.0, handwritten digit recognition plays a vital role in numerous applications such as smart banking systems and postal code detection. One of the most effective approaches to tackle this problem is through the use of machine learning and neural network models, which have demonstrated impressive accuracy and adaptability in visual pattern recognition tasks.
This Project is to develop traffic light system that can reduce traffic congestion with the aid of counters for each lane and acts wisely with the intersection in real time based with a fixed time constrain, include both hardware and software requirements using SOC FPGA technology with fundamental specification for the Register Transfer Level (RTL).
The development of a Low-Cost and Low-Power Data Acquisition System(DAQs). The DAQs will be made up of end-terminal and a gateway. The end-terminal will be micro-controller-driven device built on a SoC FPGA technology with built-in capability for machine learning. The end-terminal will be able to transmit and receive data using the Low Power Wide Area Networking (LPWAN) communication protocol that functions on LoRA.LoRa is a wireless radio frequency technology that operates in a license-free radio frequency spectrum.

The dynamic range processor is a DSP function which does as it says on the tin; it compresses the dynamic range of the incoming signal. This is used most commonly in the music industry for its effects on the perceived loudness of audio. It is also used extensively in hearing aids to compensate for the user’s reduced dynamic range of hearing. In this project a hardware accelerator is developed for the purpose of dynamic range compression of digital audio. This accelerator will be implemented in a mixed-signal infrastructure.
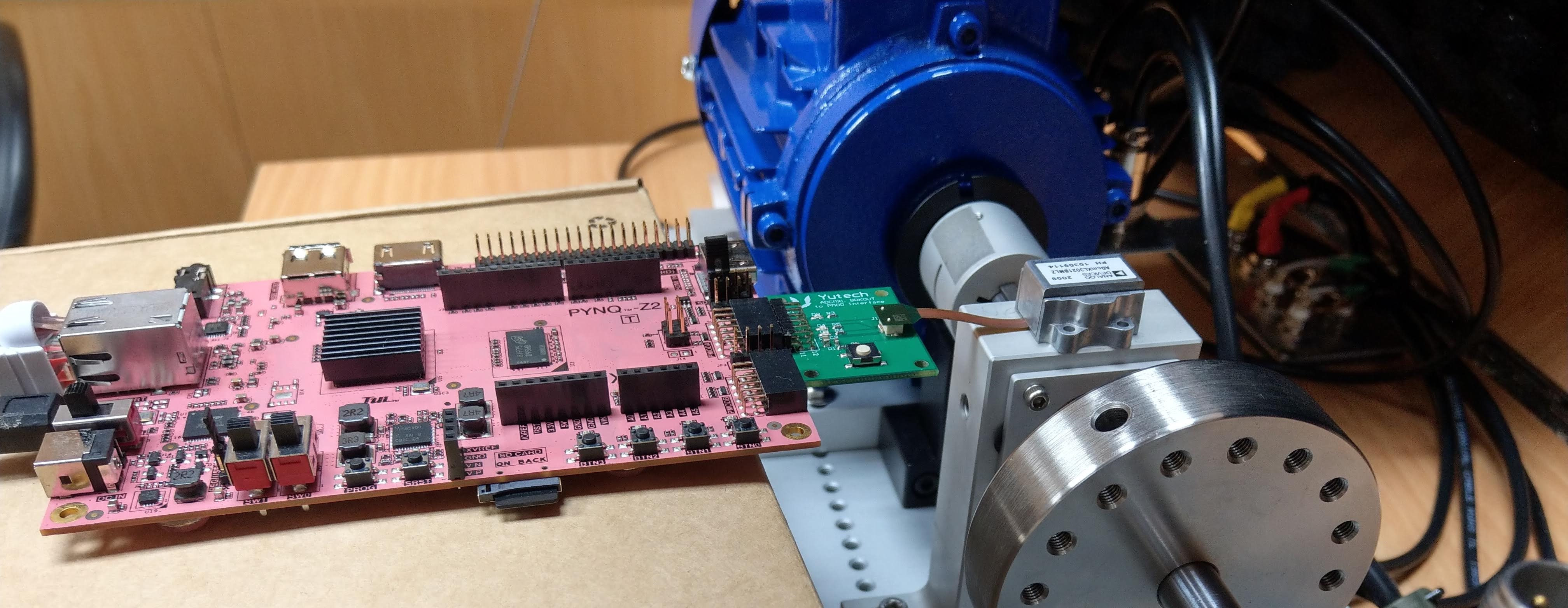

Systolic arrays are critical in parallel computing. They efficiently accomplish tasks like matrix multiplication and signal processing by coordinating a grid of processing components to perform synchronized operations. The structured data flow reduces memory access while increasing processing, resulting in substantial speedups. Systolic arrays are used in a variety of domains, from AI model training to scientific simulations, to improve speed and enable complicated computations that typical sequential approaches struggle with.
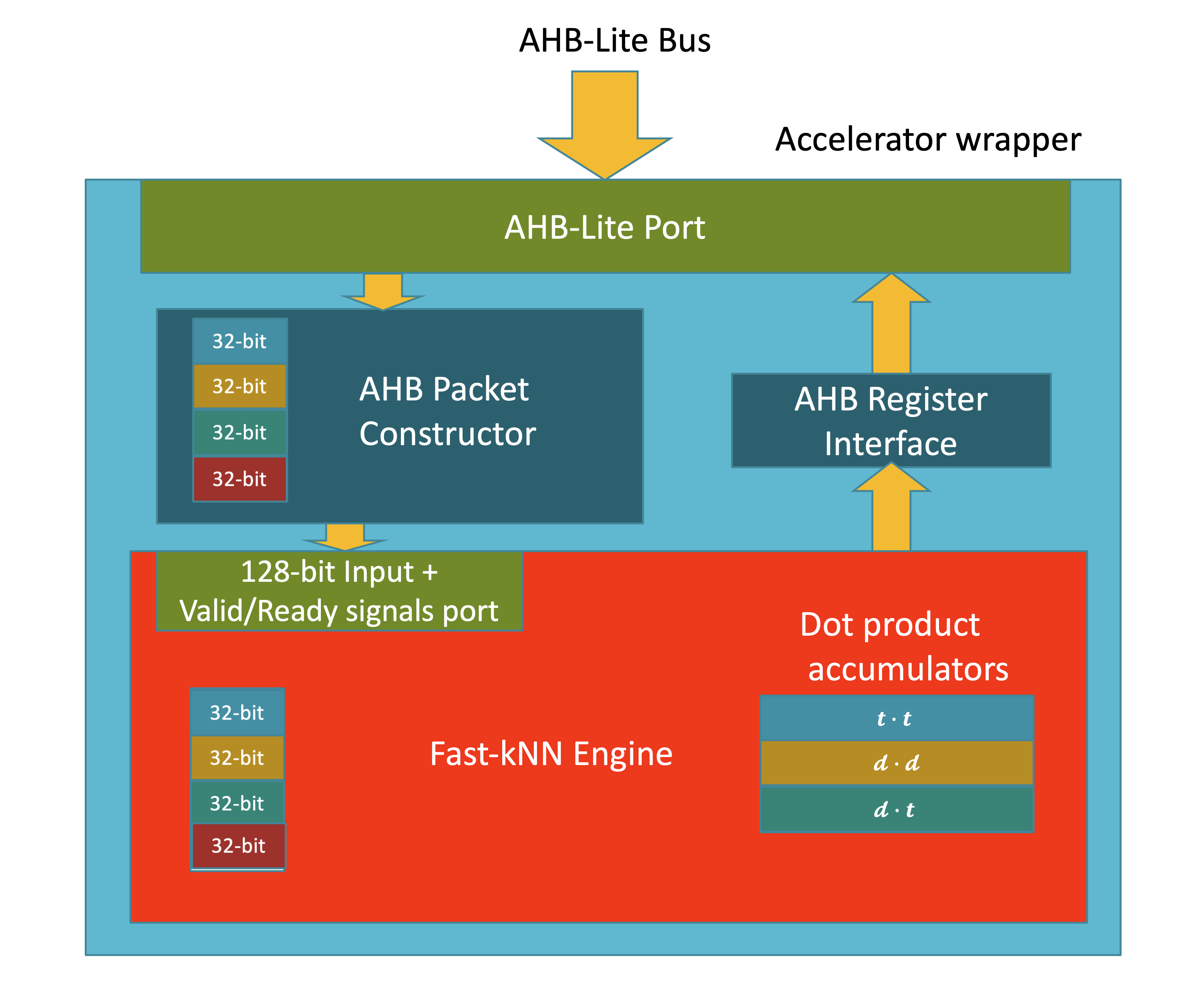
The k-Nearest-Neighbours (kNN) algorithm is a popular Machine Learning technique that can be used for a variety of supervised classification tasks. In contrast to other machine learning algorithms which "encode" the knowledge gained from training data to a set of parameters, such as weights and biases, the parameter set of a kNN classifier consists of just labelled training examples. Classification of an unlabelled example takes place by calculating its Euclidean distance (or any other type of distance metric) from all the stored training examples.
 Fidel Makatia
Fidel Makatia
 The Anh Nguyen
The Anh Nguyen
 AFOLAYAN, ABDULSAMAD
AFOLAYAN, ABDULSAMAD
 Ayodeji Oluwatope
Ayodeji Oluwatope
 Peter Richards
Peter Richards
 Kun-Chih (Jimmy) Chen
Kun-Chih (Jimmy) Chen
 Srimanth Tenneti
Srimanth Tenneti
 Epifanios Baikas
Epifanios Baikas