
People
Known Good Dies
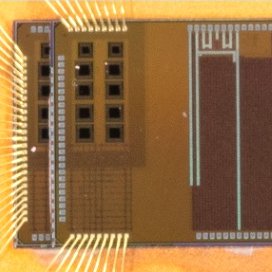
Low-cost 3D die stacking using near-field wireless communication.
This two-tier SoC, fabricated using a TSMC 65nm process, incorporates two Arm Cortex M0 CPU cores in addition to a wireless vertical AHB lite bus for inter-layer power and data transfer. The wireless AHB-Lite bus consists…
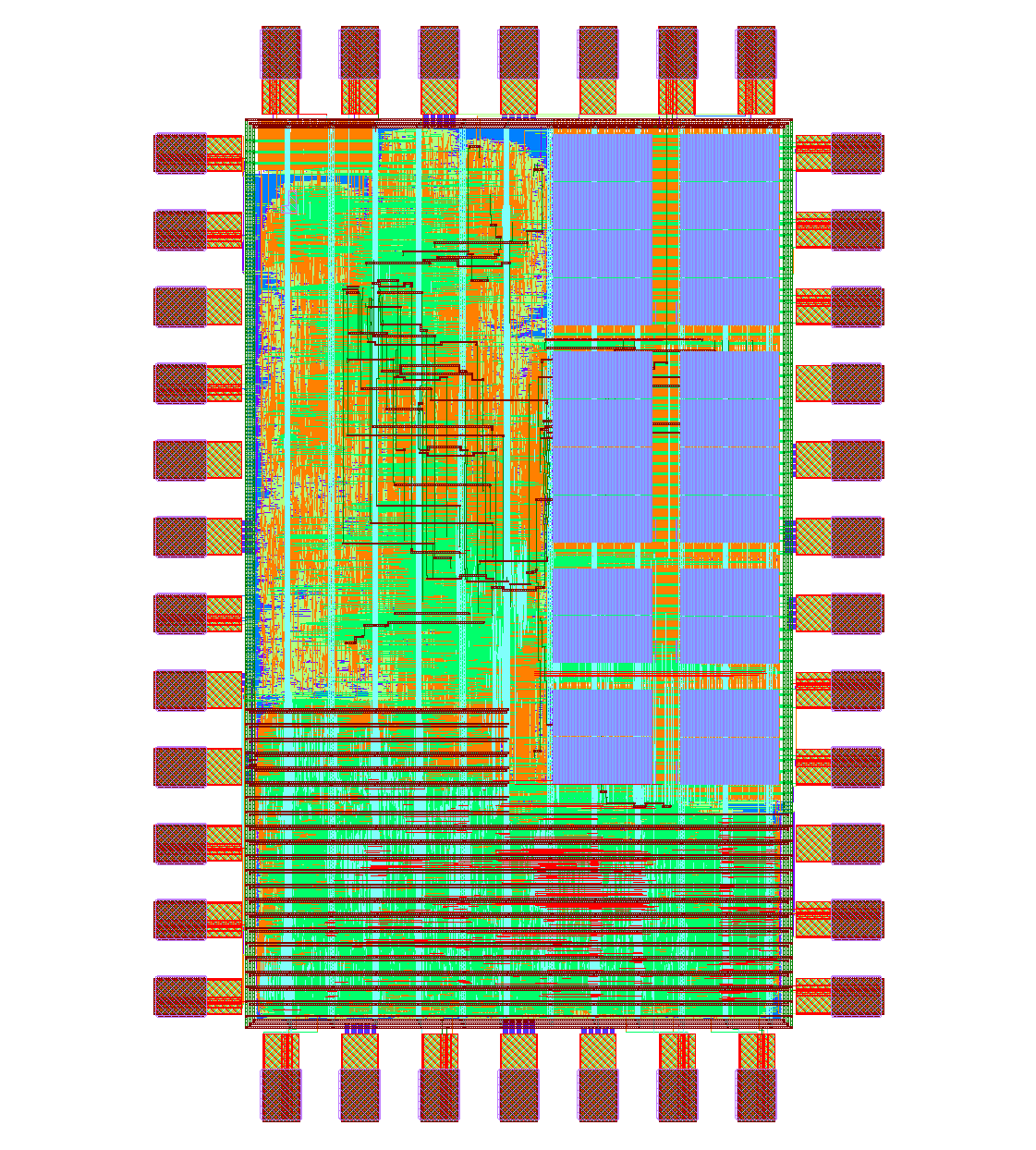
The first tape out of the nanoSoC Cortex M0 based SoC Reference Design. This reference design provides a simple microcontroller system appropriate to host and support the development and evaluation of research IP blocks or subsystems. It supports seamless transition from FPGA to physical silicon …
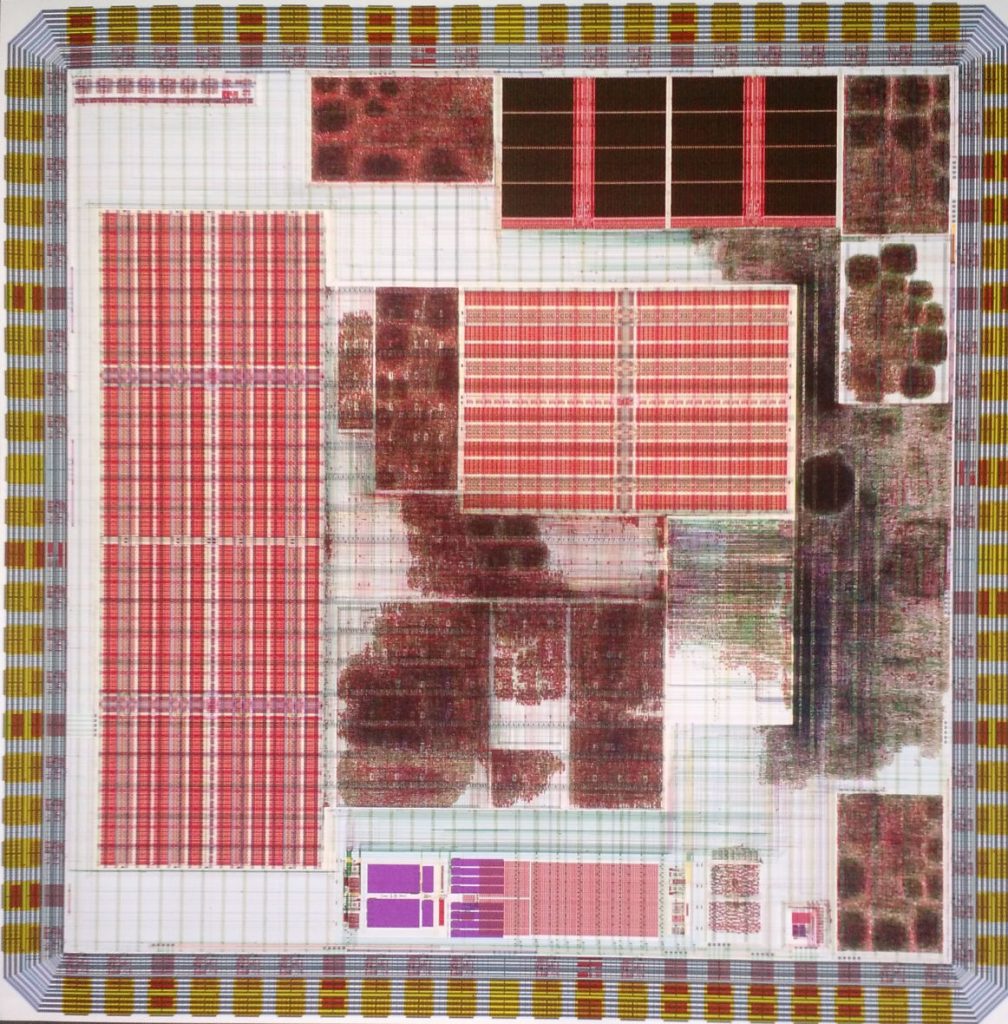
Pipistrelle-4, is the latest in a series SoCs for demonstrating multiple student projects in low-energy systems. Various circuit/system ideas from multiple researcher focusing on energy and performance with optimised SRAM bitcell and low-area overhead energy-efficient flip-flops.
P…
Projects
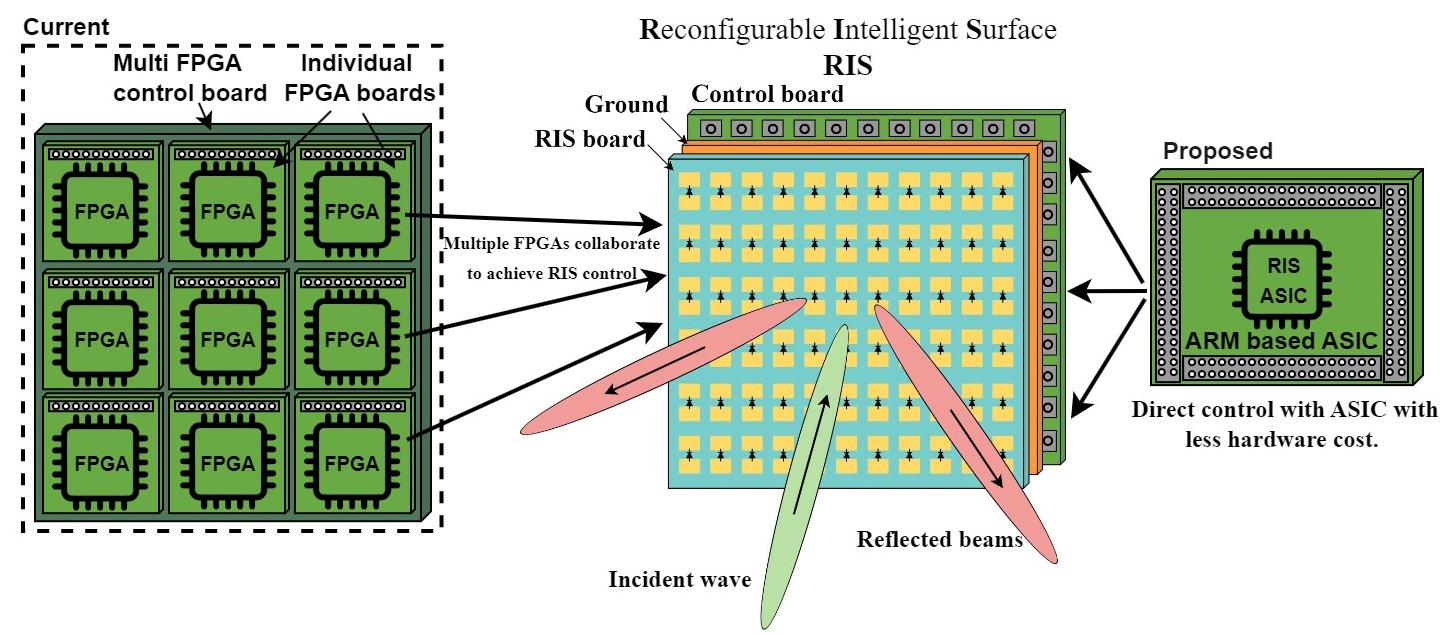
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) are planar structures composed of large arrays of tunable elements that can dynamically redirect, reflect, or shape wireless signals in the environment.
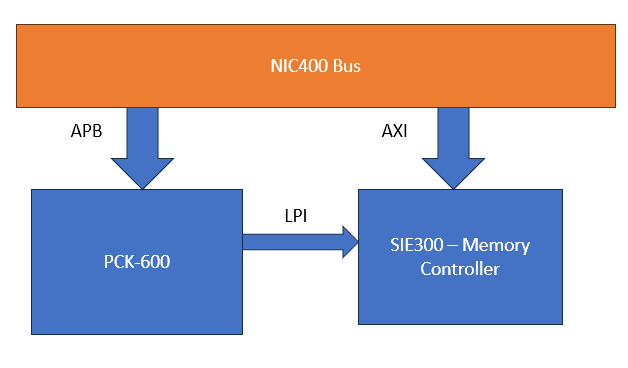
The PCK600 Arm IP provides components to allow a power control infrastructure to be distributed in a SoC in order to make a design energy efficient. Arm provide the IP as part of their Power Control System Architecture that can be used to control the power states of various parts of the system. This control of the power infrastructure is achieved through the use of the Power Policy Unit (PPU). This unit has an APB interface to allow for software control, and some low power interfaces that can connect to the power controllable IP within the system.

This program is dedicated to the development of a System on Chip (SoC) platform, specifically designed to support learning and research activities within Indonesian academic institutions. The platform serves as an educational and research tool for students, lecturers, and researchers to gain hands-on experience in digital chip design.
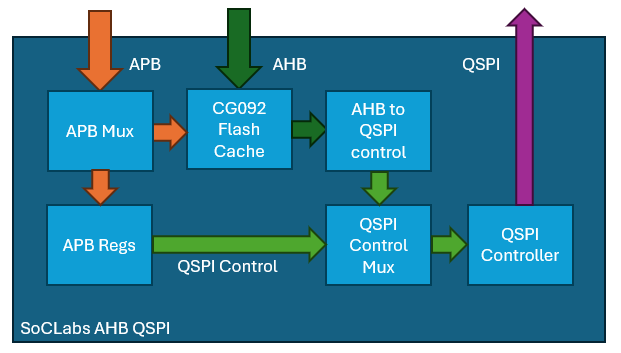
The instruction memory in the first tape out of nanosoc was implemented using SRAM. The benefit was the read bandwidth from this memory was very fast, the downside was on a power-on-reset, all the code was erased as SRAM is volatile memory. An alternative use of non-volatile memory would benefit applications where deployment of the ASIC does not allow, or simply time is not available for programming the SRAM after every power up.








 Zhicheng Shen
Zhicheng Shen
 Daniel Newbrook
Daniel Newbrook
 Trio Adiono
Trio Adiono