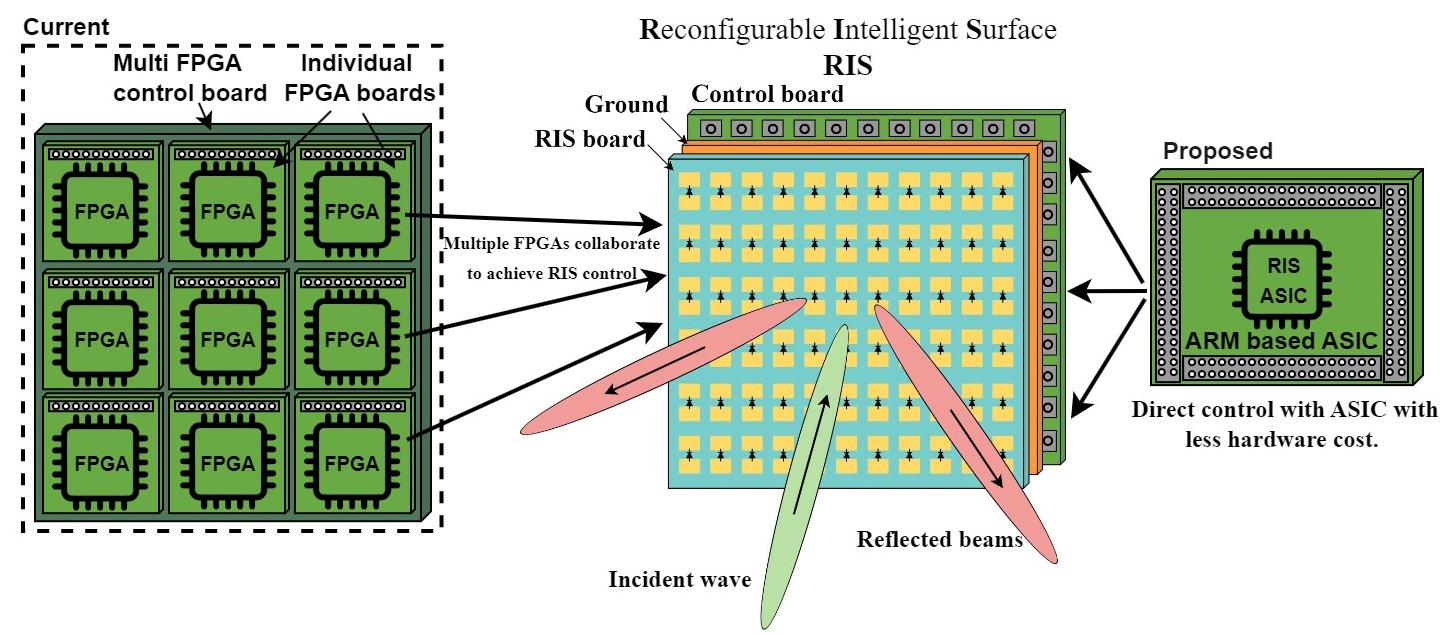
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) are planar structures composed of large arrays of tunable elements that can dynamically redirect, reflect, or shape wireless signals in the environment.

Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RIS) are planar structures composed of large arrays of tunable elements that can dynamically redirect, reflect, or shape wireless signals in the environment.
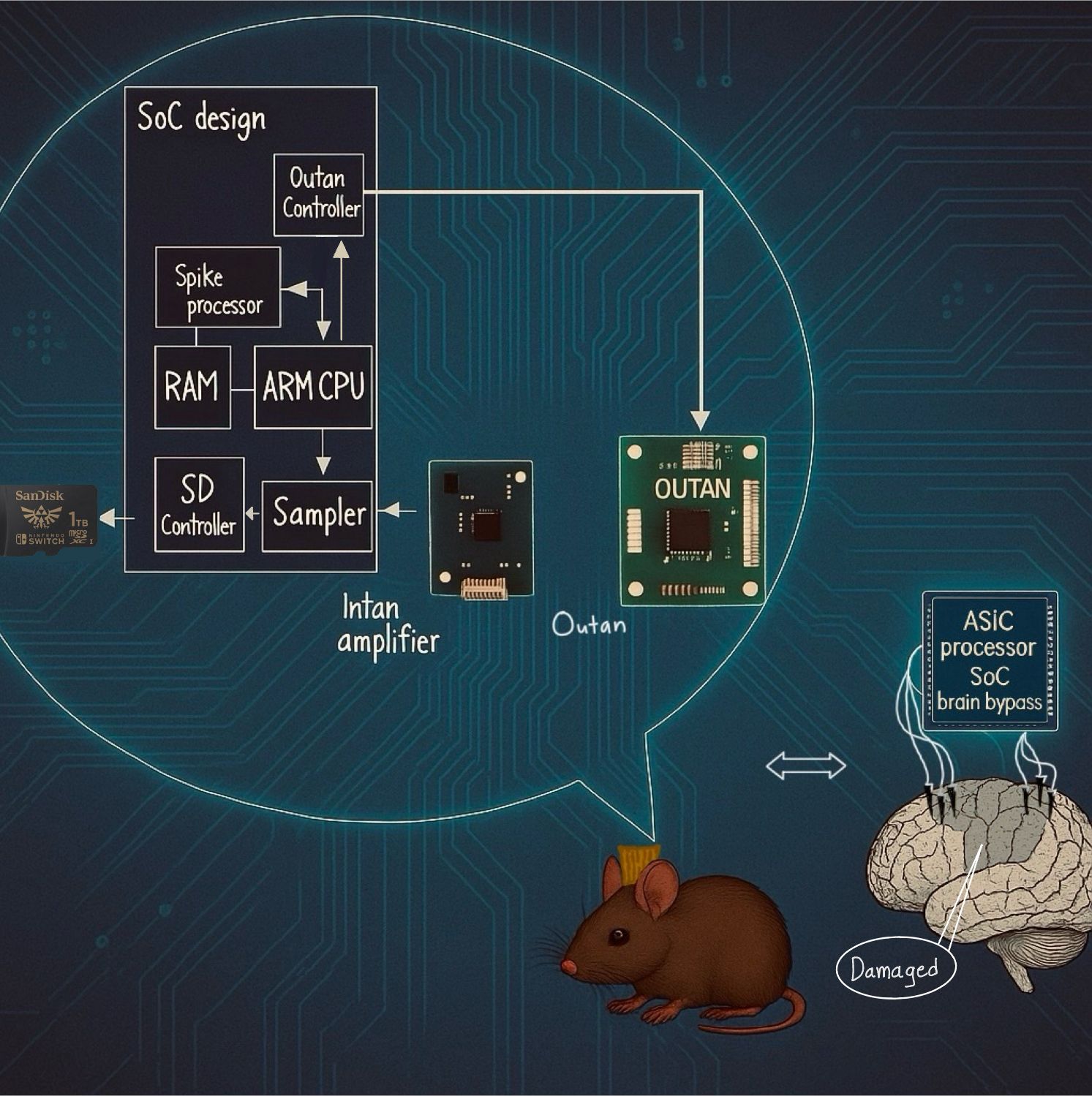
Stroke and epilepsy are among the most common debilitating neurological conditions, with a worldwide prevalence of 100 million people (World Stroke Organization, 2022) and 50 million people (World Health Organization, 2024), respectively. Present-day approaches for treating neurological and neurosurgical conditions include physiotherapy, pharmacological treatment, surgical excision, and interventions such as deep brain stimulation.
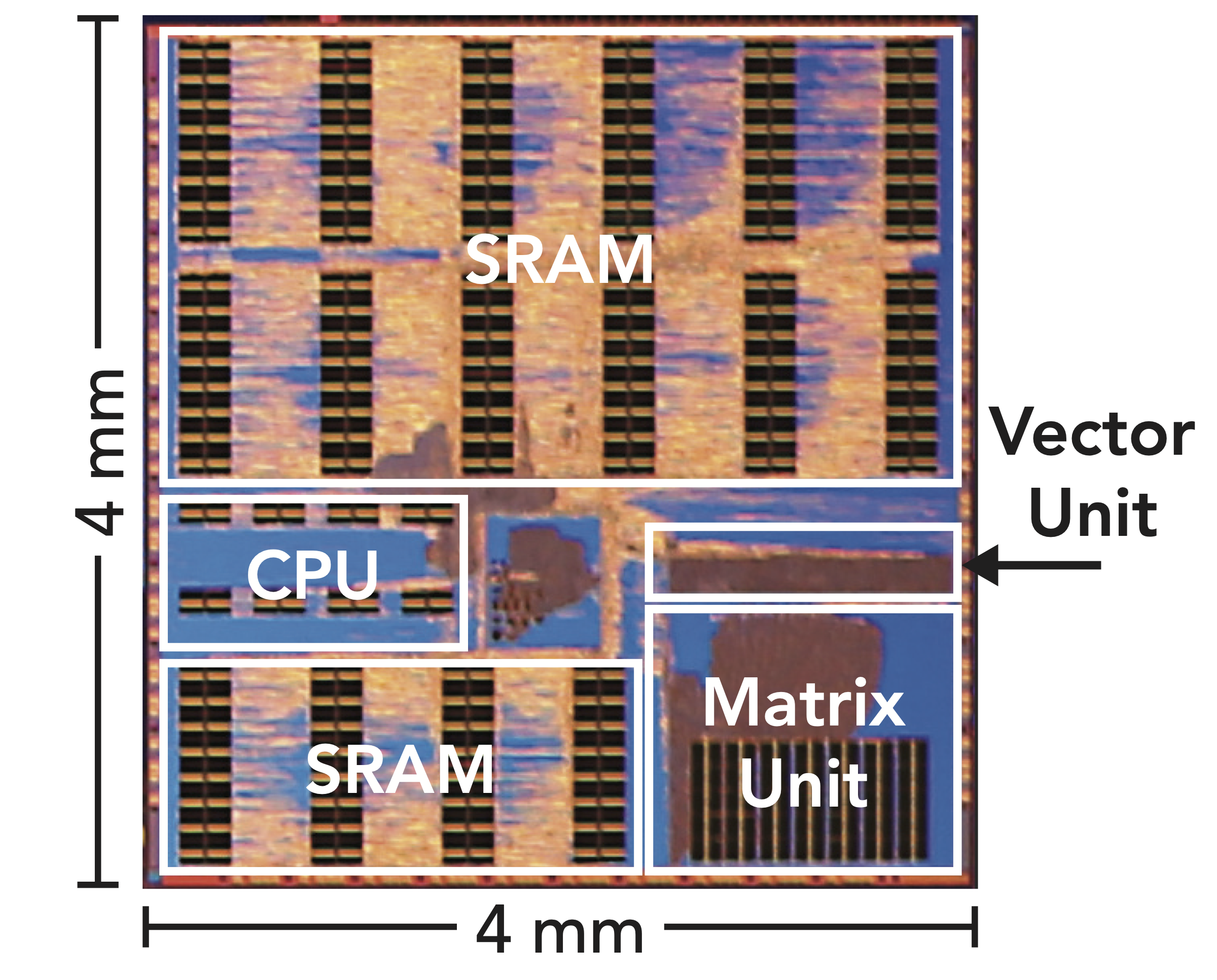
Aspen is a unified accelerator for deep neural network (DNN)-based extended reality perception workloads. Aspen proposes a mixed-precision quantization scheme using the posit datatype to reduce memory usage while maintaining accuracy, a DNN accelerator for mixed-precision posit datatypes, and efficient data prefetching and data layout to minimize data reorganization. The Aspen system-on-chip has an Arm Cortex-M3 CPU, a mixed-precision posit-based DNN accelerator, and 4 megabytes of SRAM partitioned into eight 512 KB banks, connected through a 128-bit-wide interconnect.
Project Overview:
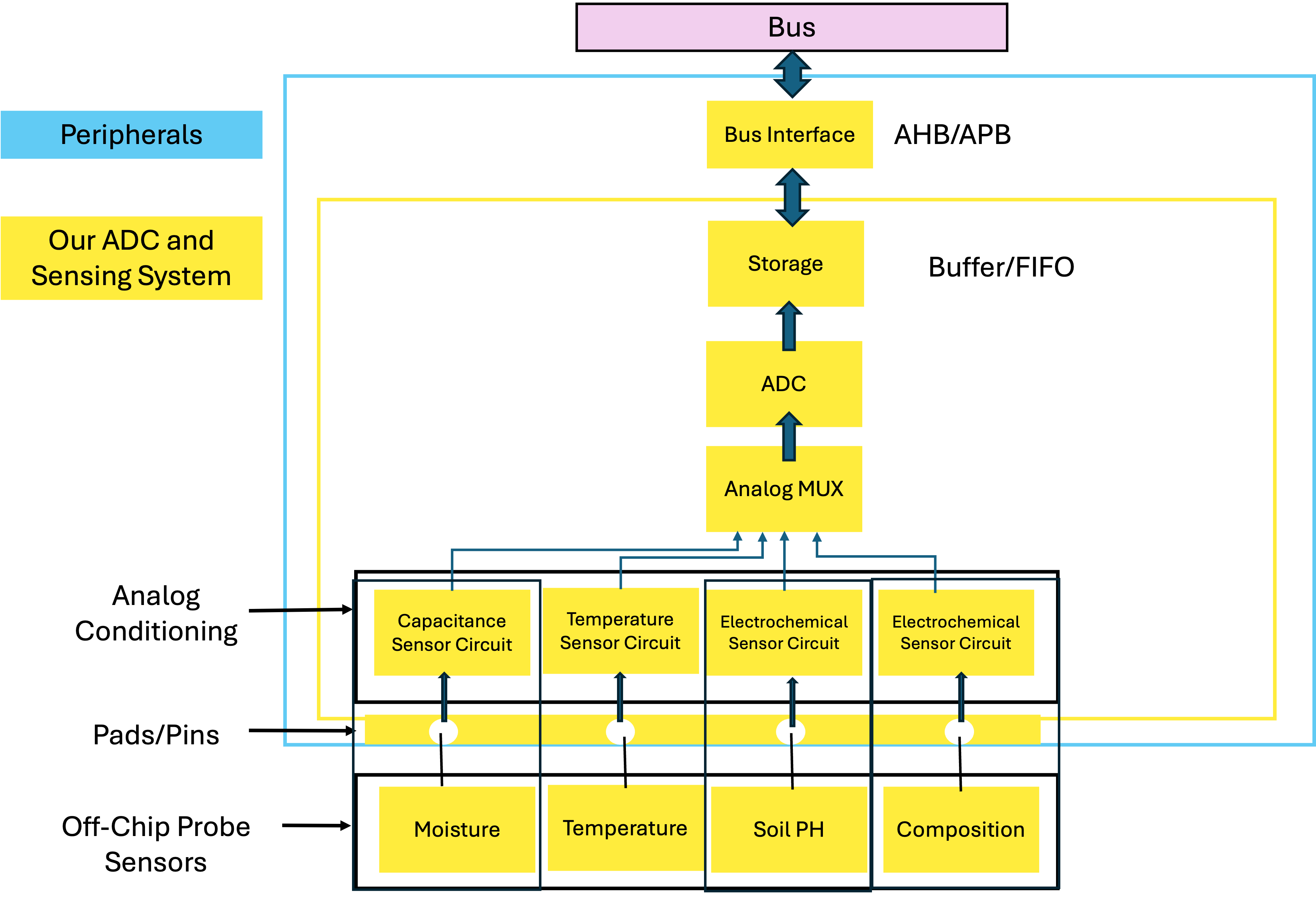
Our innovative SoC design for precision agriculture revolutionizes field management by deploying a robust mesh network of sensor-based devices, capable of detailed monitoring and swift response to variations in soil health, erosion, drought, and pest activities. This system not only ensures reliability through its mesh architecture—eliminating single points of failure—but also incorporates diverse sensors for comprehensive data acquisition. It's engineered for energy efficiency to sustain operation throughout an entire crop season, significantly optimizing resource use and reducing waste.
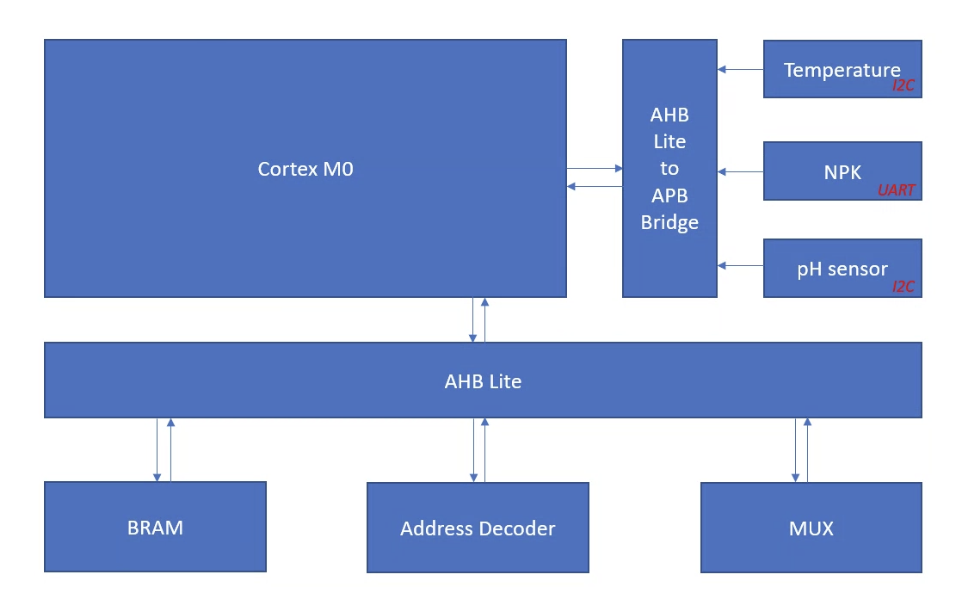
This project focuses on developing a plant growth monitoring system for space exploration missions using the ARM Cortex-M0 microcontroller core. The projects aim to develop a SOC based on ARM M0 core for interactive plant monitoring by interfacing AHB lite, GPIO, timers, and communication protocols such as UART, I2C, SPI, and co-processors. This project also proposes two co-processors for interactive plant monitoring and control. One AI co-processor for classification and prediction of plant and environmental data.
Nowadays, rotating machine is the power source for most production equipment and is widely used in manufacturing factories. Common rotating machinery mainly includes bearings, gears, shafts, and the others. However, rotating machines suffer from frequent collisions and vibrations which lead to wearing and aging, which increases the chance of failure in the overall system operation. This make the cost of factories increase and the quality of production deteriorate. Therefore, the industries gradually value the usage of accurate and efficiency predictive maintenance system.
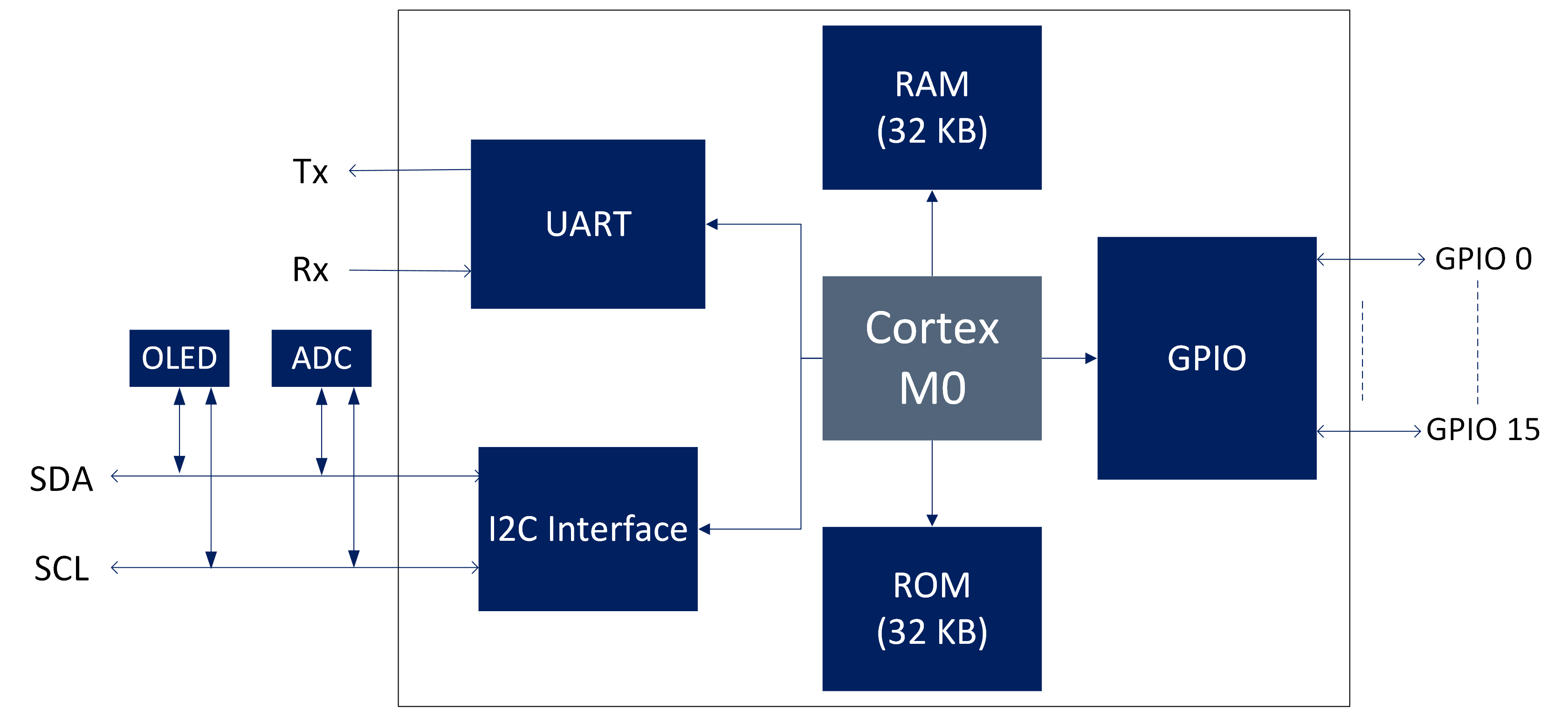
Conventional healthcare is expensive and reliant on the physical presence of the patients. Continuous health monitoring tracks vital health parameters like heart rate, blood pressure, etc. While these work well in measuring the parameters, modern-day devices rely on the cloud to compute and interpret data. This results in an increase in data transfer between the device and the cloud, and if this connection breaks, there can be no interpretation of data. Hence, there is a need to shift the computation to the hardware, referred to as "Edge Computing".
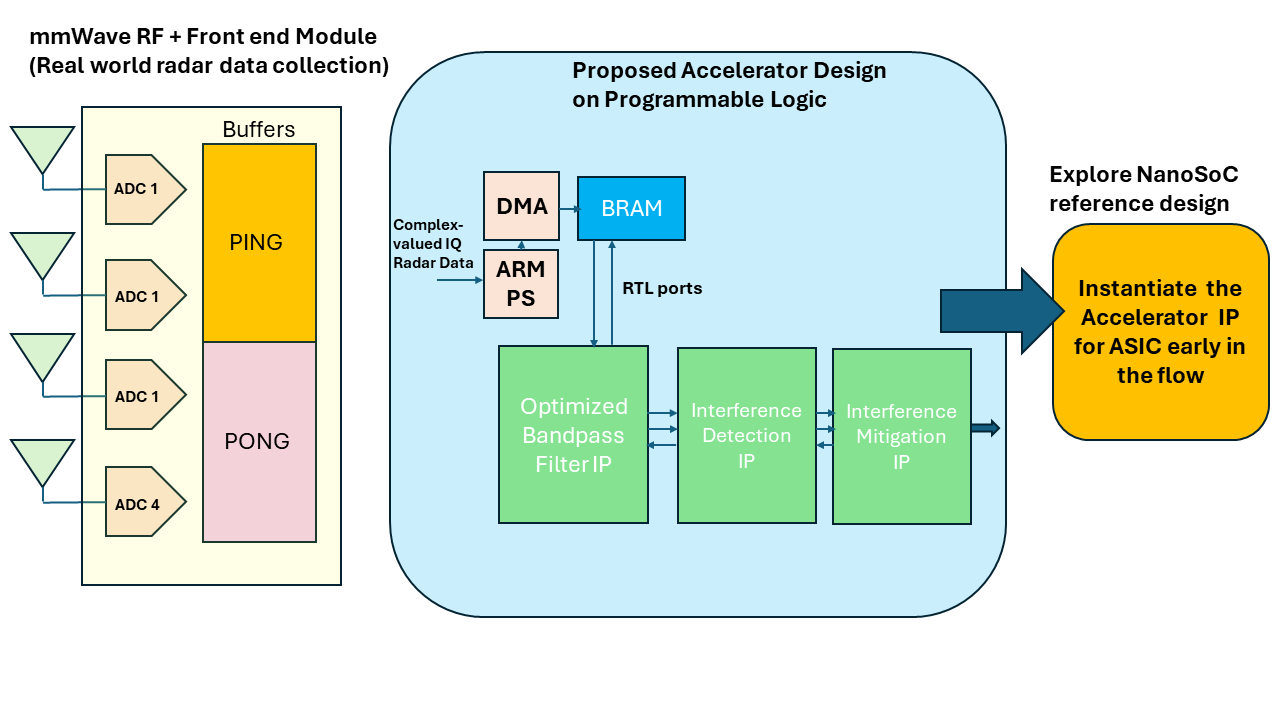
Advancements in electronics, wireless communications, and sensing technologies have made possible a multitude of smart sensing features in automotives. Integrating high-frequency sensors, digital signal processors and hardware accelerator engines on a single system on a chip (SoC) enhances sensing computation potential of radar sensors utilized in automotives.
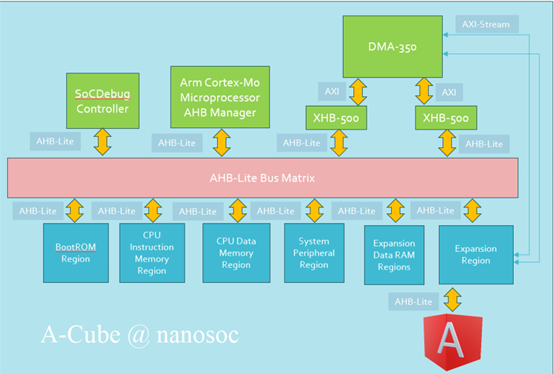
We propose the A-Cube design methodology to create medical decision support on the edge. The design and implementation of an atrial fibrillation detector hardware core was selected as a proof-of-concept study. To facilitate the required atrial fibrillation functionality, we adopted an established AI model, based on Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) technology for hardware implementation. The adaptation was done by varying design parameters such as data window and the number of LSTM units.