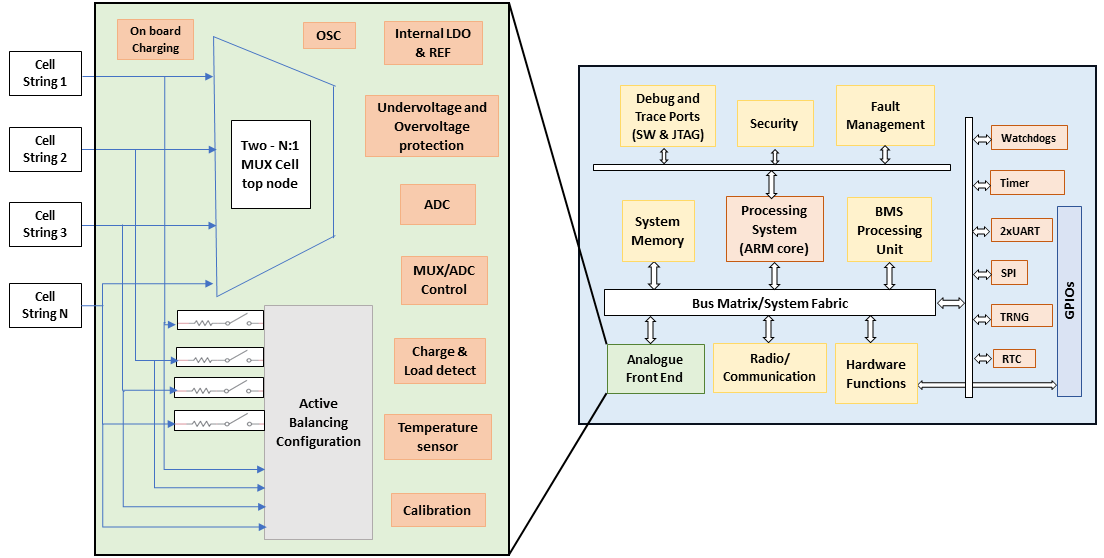
Battery storage systems are an important source for powering emerging clean energy applications. The Battery Management System (BMS) is a critical component of modern battery storage, essential for efficient system monitoring, reducing run-time failures, prolonging charge-discharge lifecycle, and preventing battery stress or catastrophic situations. The BMS performs functionalities such as data acquisition and monitoring, battery state estimation, cell equalization, and charge protection, making it computationally intensive to manage large scale battery storage.

 Rashi Dutt
Rashi Dutt
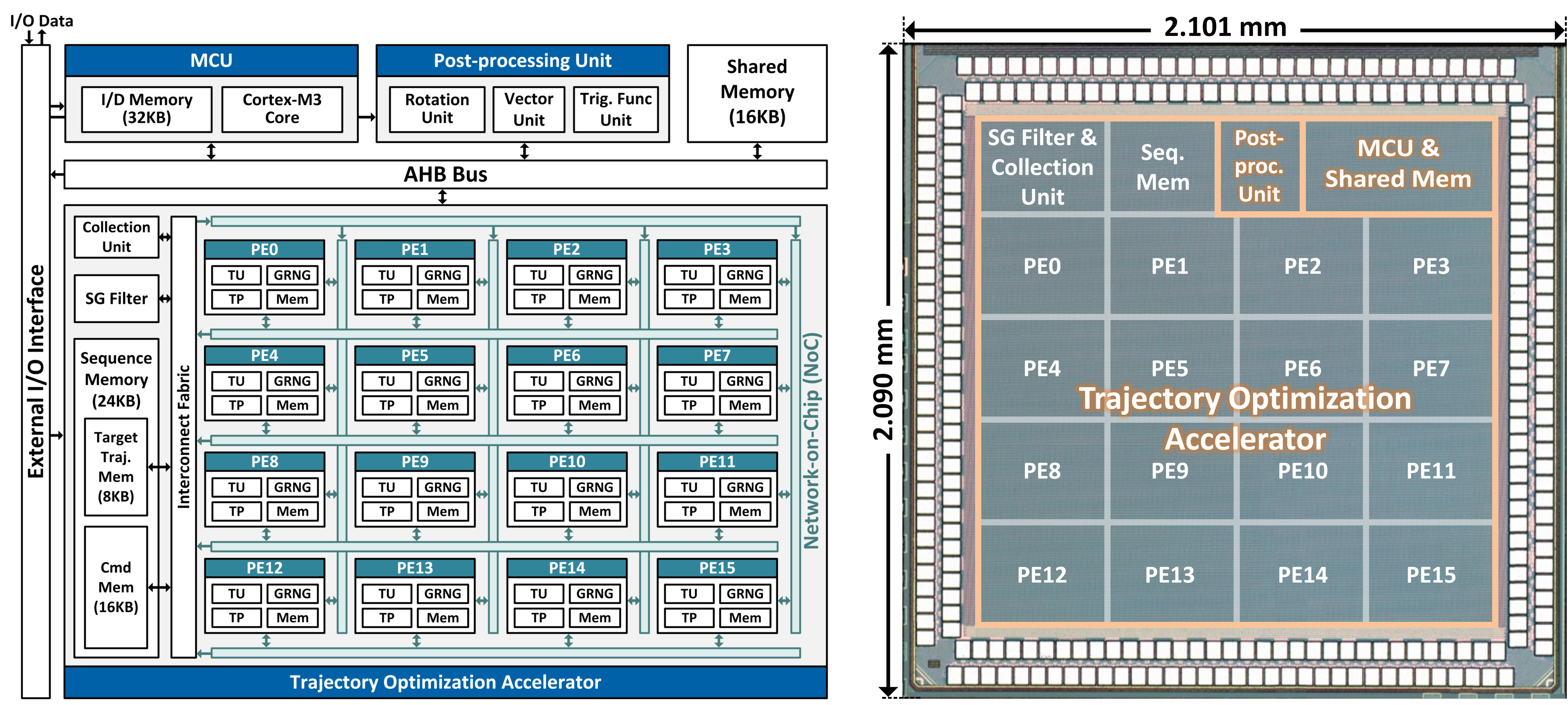
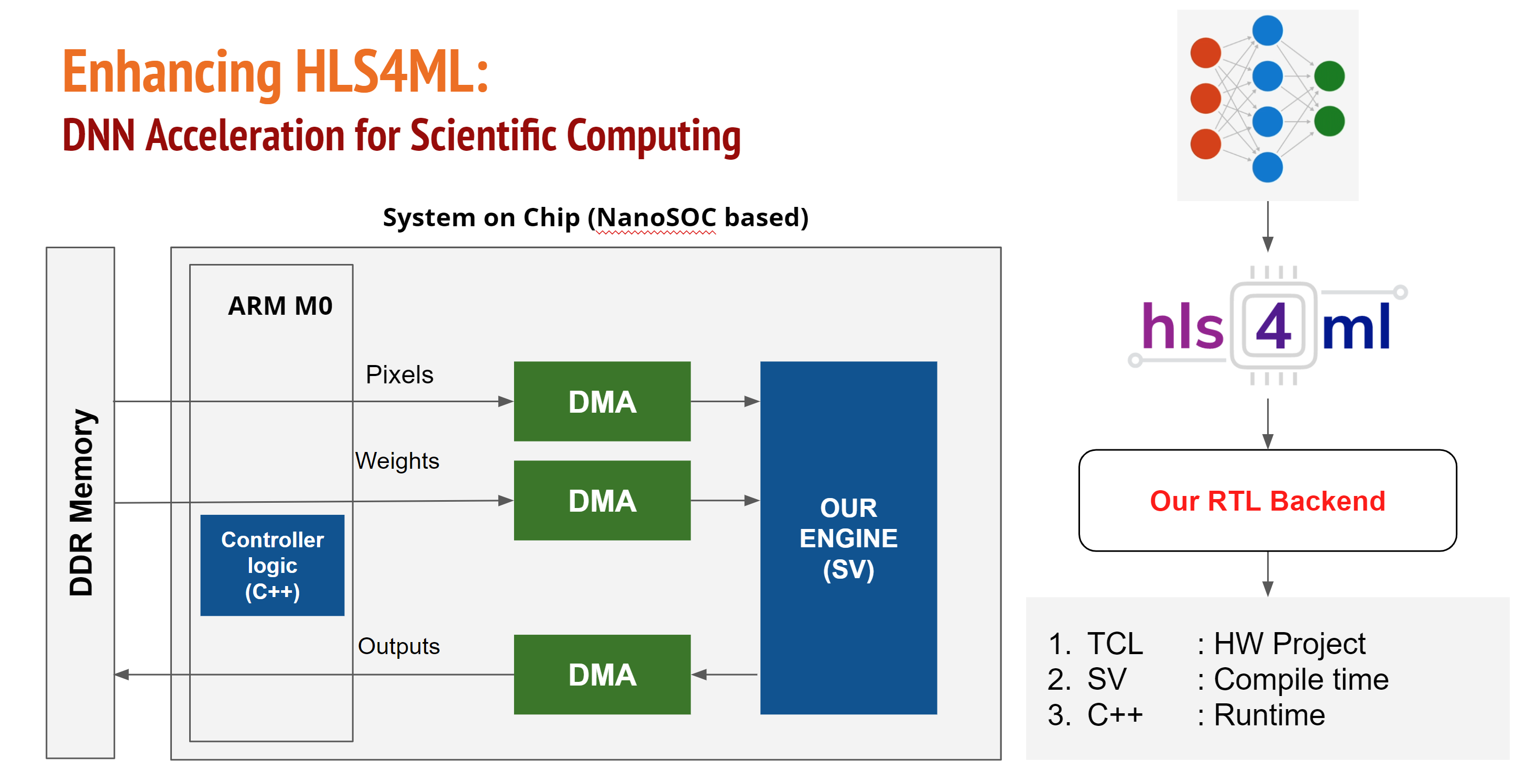

 Abarajithan Gnaneswaran
Abarajithan Gnaneswaran
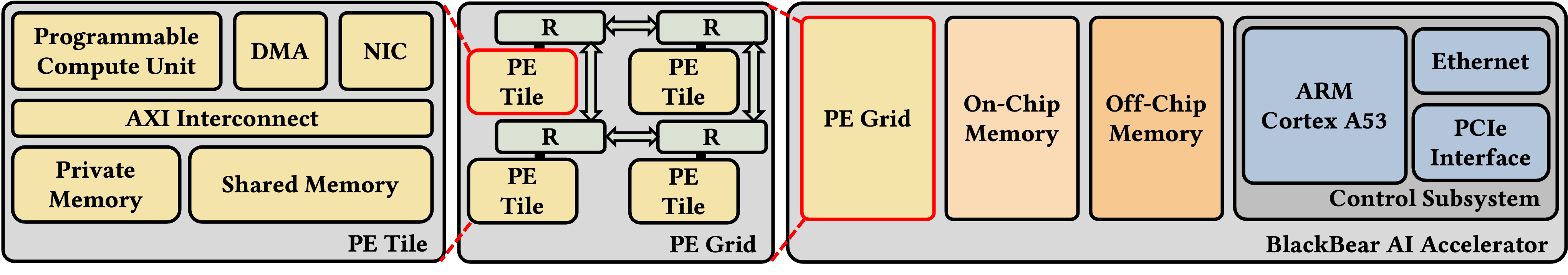
 Amit Acharyya
Amit Acharyya